
The Automotive API: Use Cases & Benefits
Learn how to leverage the Automotive API to reduce software development costs, fix issues with dependencies, facilitate integrations, elevate customer experience, and unlock new revenue streams.
Previously, we discussed how to address hardware and software decoupling challenges in SDV development. This blog post focuses on the Automotive API concept and how it can be applied to resolve data fragmentation and integration issues, as well as the benefits and use cases it has to offer.
Introduction to the Automotive API
The Automotive API is an interface that enables standardized, data-centric communication for vehicles with both onboard components and external applications. It outlines how other systems can securely access vehicle data in a unified, manufacturer-independent way, which can then be used to integrate third-party solutions and services into the vehicle.Automotive API has become an answer to many challenges in designing software-defined vehicles.
Before diving deeper into the use cases and benefits of the Automotive API, let’s explore the technological foundation of the concept.
3 Core Components of Automotive API
AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform
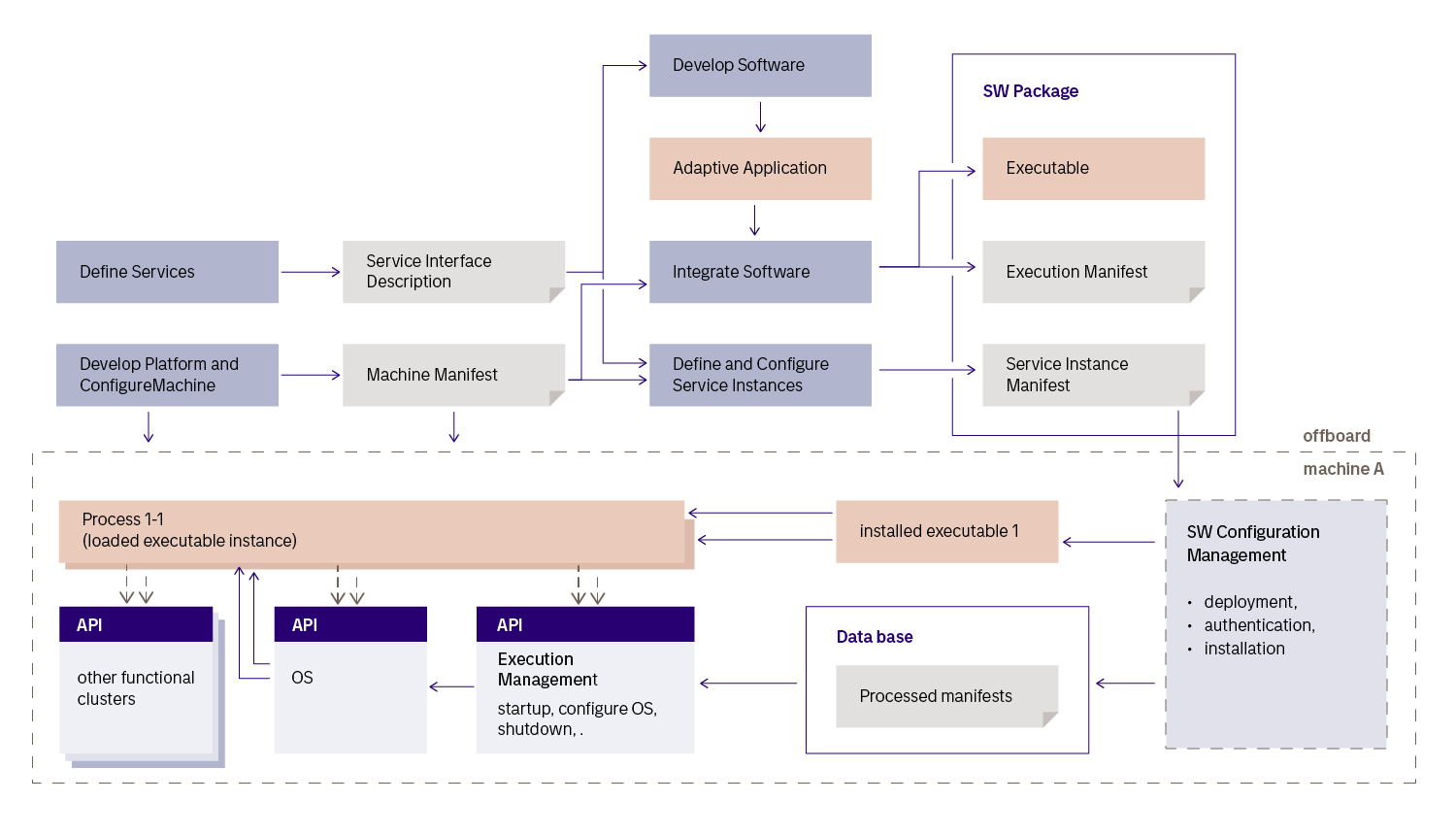
While AUTOSAR Classic focuses on traditional ECUs, AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform (AP) is a more complex standardized software architecture for deeply embedded, high-performance ECUs that enable OTA updates, ADAS, and other sophisticated automotive features. AP is based on SOA to enable better flexibility and scalability for complex applications. The platform leverages a POSIX-compliant operating system as well as ara::com – API signatures that abstract communication within AP.
When utilizing AUTOSAR Adaptive, software architects create definitions for the services, which then generate C++ interfaces that have to be implemented. During the later development phase, new protocol-specific code components are created so that the engineering teams are independent of the future network communication layer.
In addition to abstracting communication layers, AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform also provides the capabilities to abstract persistence, update, configuration, execution, and state management.
AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform Development Workflow
Vehicle Signal Specification (VSS)
To make vehicle data accessible for the Automotive API, there needs to be a common data model that defines the syntax and semantics of the vehicle data. The Vehicle Signal Specification (VSS), introduced by the Connected Vehicles System Alliance (COVESA), was chosen as such a common model.
VSS is an approach that describes vehicle data in a standardized manner, thus reducing data fragmentation, fostering data interoperability, and facilitating collaboration with other industries. In essence, it acts as a shared language between the vehicle and the solutions and services offered by third parties. The extensive catalog of vehicle signals of VSS can be used as a reference when vendors agree on what vehicle data their service needs signals from.
Vehicle Information Service Specification (VISS)
A communication protocol is required to facilitate access to the Automotive API network interface, which uses the VSS data model. To make it possible, the Vehicle Information Service Specification (VISS) was applied. VISS is a protocol that enables secure and legitimate communication and access control to data through the Automotive API. Users can request vehicle data using the Automotive API Gateway (VISS interface that uses a specific VSS catalog). The purpose of the Gateway is to abstract the platform architecture for the applications that use VISS/VSS. When vehicle data is requested from the VSS catalog, the Gateway recognizes where it can be obtained, which platform-specific services have to be queried, and how the data must be converted.
Automotive API in the AUTOSAR Ecosystem
The convergence of AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform with VSS and VISS has formed the Automotive API, which allows seamless and secure access and exchange of vehicle data with both AUTOSAR partners and third-party organizations. The concept is an important contribution to the global ecosystem of connected vehicles, which fosters innovation and compatibility across vehicles and external software solutions, as well as unlocks a full range of valuable business use cases.
Automotive API within the Vehicle Architecture
Automotive API Use Cases
Smart Devices & Mobile Applications
Automotive API can be used to establish connectivity between the vehicle and smart devices via short-range communication technologies, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi access points. Long-range connections are also possible via the cloud and the Automotive API, which is partially deployed in the vehicle and provides data to the VISS server. Direct access to vehicle data from smart devices can significantly improve user experience, while also minimizing latency.
Ultimately, such connectivity allows the use of smartphones and custom mobile applications, which interact with the vehicle’s Human Machine Interface (HMI), and enable a variety of advanced functions, such as:
- Unlocking or starting your vehicle remotely
- Using infotainment apps in the car’s dashboard.
Vehicle Data & Specifications
With the Automotive API, developers can engineer a range of vehicle-related services, such as viewing data history reports that indicate the number of previous owners, traffic accidents and mileage, without the knowledge of platform architecture. Furthermore, there’s an option to check a range of vehicle specifications, including model, engine type, in-vehicle equipment, and more. These use cases are beneficial for both automotive dealerships and their clients who are searching for the best-case purchase.
Repair & Maintenance
Developers can use the Automotive API to help notify the users when the vehicle needs to be repaired or requires maintenance. With such a service, drivers can view the vehicle parts that have to be fixed, as well as see the estimated time and costs for the technical services.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS)
Automotive API can provide access to a range of MaaS services for drivers, vehicle dealers, and third parties. Dedicated mobile apps can be integrated with the vehicle to enable on-demand mobility services – from renting a car, or choosing more sustainable transportation options to planning, booking, and paying for a trip.
Automotive Insurance Services
By utilizing the Automotive API, insurance companies can significantly improve the underwriting process and diversify their service offerings. For example, by accessing various types of vehicle data and analyzing the driver’s profile, insurers can determine whether the driving style is aggressive or not, or how often the driver is involved in car accidents. This data can then be used for evaluating risks during underwriting or adjusting the insurance policies.
Integration of In-Vehicle Subsystems
The architecture of modern vehicles is rather sophisticated as it includes many subsystems, such as AUTOSAR and Android Automotive, which coexist under the hood. Each subsystem has its inherent complexities that create a range of integration issues. Automotive API can unify and simplify the accessibility and integration of these subsystems.
Benefits of the Automotive API
- Standardized access and exchange of vehicle data, which reduces the development costs for OEMs
- Opportunities for automotive players to diversify their service offerings and unlock new revenue streams
- Enhanced customer experience through advanced in-vehicle capabilities and external services
- Improved transparency and customer trust with access to accurate vehicle data and specifications
- Spared time, costs, and resources for automotive software integrations
- Fixed issues with dependencies, which improves SDV updatability, enables integration with IVI and cloud-based services, or even solutions that can “talk” to any car without extra development efforts
Conclusion
The role of automotive software rapidly grows and catalyzes the shift to next-gen SDV vehicles and V2X connectivity. Now the road to SDV vehicles is paved with a range of challenges, most of which can be navigated with virtualization and service-oriented architectures, while the remaining technical obstacles can be resolved with standardized vehicle data models and the Automotive API.
In addition to empowering OEMs with significant time and cost savings by enabling a standardized and manufacturer/vehicle-independent way to access data, the Automotive API concept also provides a wide spectrum of valuable use cases for the entire automotive value chain.
OEMs and third parties can drive revenue with new in-vehicle services, whilst customers can enjoy a more convenient, safe, and entertaining driving experience.
As a leading Nordic digital services and software company with 24,000 experts globally, Tietoevry Create can help you apply the Automotive API to extend your vehicles with value-added services and reduce your development costs.
Furthermore, Tieotoevry offers a holistic portfolio of other automotive software services, ranging from expert consulting, embedded software development, middleware, BSP, firmware, and custom integrations to vehicle connectivity testing and cybersecurity.
Contact us to optimize costs and elevate your in-vehicle experience with Automotive API!

Piotr is an experienced software developer in the area of mobile devices, starting his career with the old QC platform called BREW, then moving on to SymbianOS, and finally Android. For the past three years, Piotr has explored the marriage of Android and the world of automotive. Multiple automotive R&D projects have covered for example voice and audio processing for voice assistant – implementing automotive use cases on the early Android Automotive platform. Piotr is passionate about contributing R&D work around specific Android Automotive requirements and solutions.

Paweł is a C++ senior software developer specializing in embedded systems for the automotive domain and experienced in working with a wide range of embedded Linux platforms. He has also gained professional experience in the biomedical industry. One of his most challenging and rewarding achievements was contributing to the specification of the Automotive API within the AUTOSAR consortium.



