
Can I Trust Third-Party Automation Solutions in My Network?
Finding the balance between convenience and security
The RAN architecture defined by O-RAN Alliance, commonly referred to as ‘O-RAN Architecture’, provides – among many other things – the ability to deploy automation solutions in a standardized way.
Setting the Scene
In the best of all possible worlds , this could be a salvation for mobile network operators (MNOs) under pressure, but it could also become a severe threat for the same MNOs if not approached with consideration and care. In this blog we will elaborate on how to employ third-party automation solutions in a trustworthy way and avoid exposing ourselves to apparent risks.
The foundation for the standardized deployment of automation solutions is the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) concept, which could be seen as a RAN programming platform for applications realizing an automation solution that comes in the form of one or several ‘Apps’. Such an application does not necessarily need to be provided together with, or by the same vendor as of the rest of the RAN. There could even be Apps from several vendors that together constitute a single automation solution.
The RIC concept exposes standardized API’s that any automation logic may exercise to monitor and control the functionality and behavior of the RAN as needed to close the operational loop. These APIs enable third parties to develop intelligent automation and optimization solutions that will work with different RAN infrastructures, both native O-RAN, and mix of O-RAN and legacy RANs.
RIC Concept in O-RAN Architecture
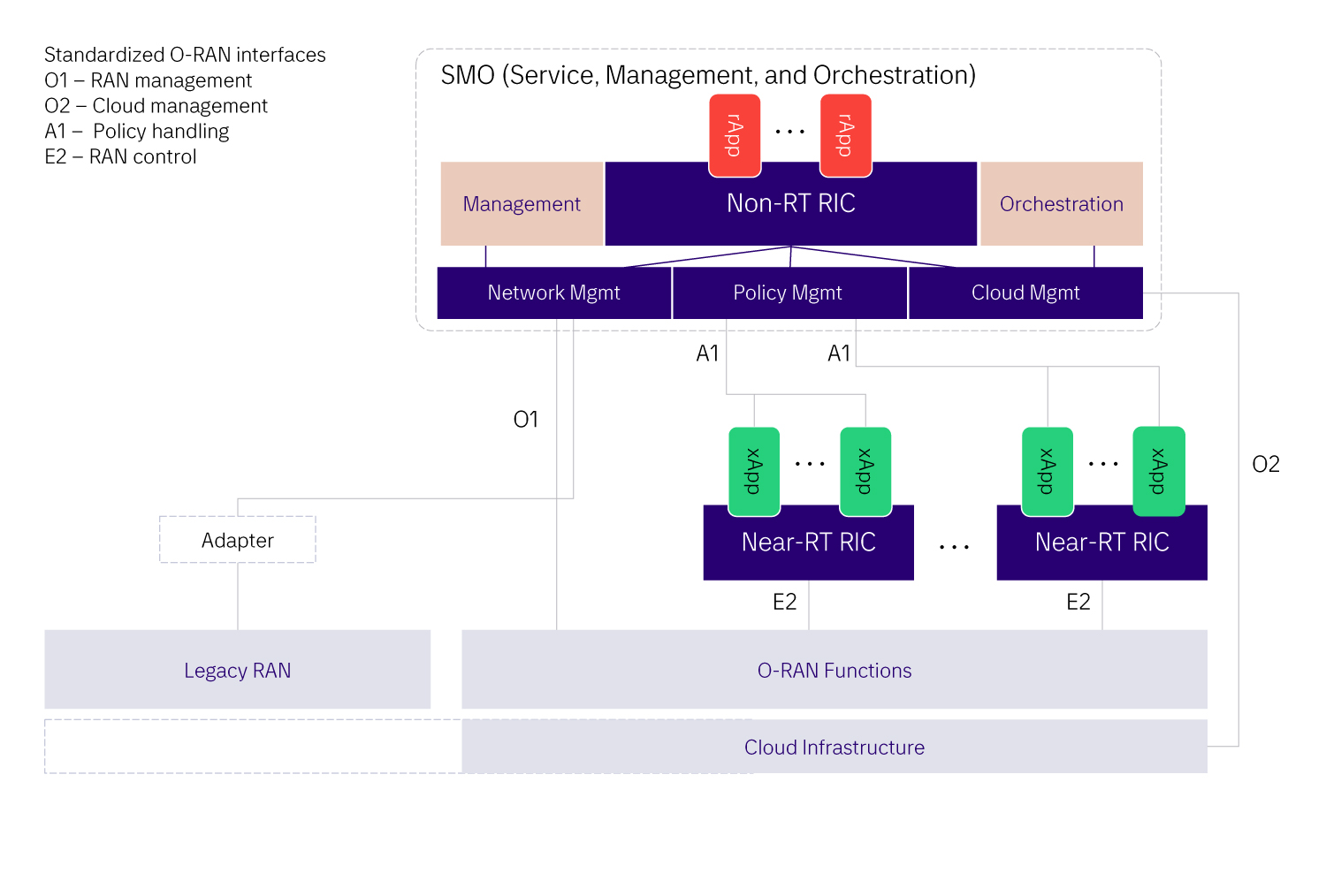
The RIC comes in two flavors that differ in their real-time (RT) capabilities: the non-RT RIC for control loop delay of more than 1 sec, and the near-RT RIC for delay between 10 msec and 1 sec . The former is designed to support the rApps that address the automation of many traditional operational procedures, embracing both O-RAN and a legacy architecture RAN. The latter – near-RT RIC – supports xApps that focus on RAN optimization and resource utilization tasks for the O-RAN.
Besides automating the normal management and orchestration functionality, rApps also have the possibility to control the behavior of xApps by installing or withdrawing policies in the xApps. xApps monitor and execute actions towards the O-RAN functionality directly over a standardized interface.
The Automation Dilemma
It is apparent that the increasingly complex network brings with it operational complexity and increases costs. We’re also approaching the point in time where it becomes impossible to operate networks the traditional way. Daily operation will require so much data and so much analysis that it goes beyond the capacity of a human.
It is also evident that the ever-growing amount of traffic and the emerging enterprise services call for investment that are hard to cash in on for most MNOs. Customers do want more capacity, but they don’t want to pay for it. So, if you can’t raise the prices for your customers, then you must use your assets (i.e., the RAN) in a more efficient way.
Throughout the mobile industry, we pin our hope on network automation as the way to hold down the cost for running mobile networks. We see network automation as a key for efficiency, scalability, and operational simplicity. It involves using software-defined solutions, machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time analytics to automate the operation, monitoring, optimization, and troubleshooting of network functions. This reduces the reliance on human labor and speeds up processes that traditionally take much longer to manage manually.
One of the prime drivers for deploying O-RAN networks, both natively and side-by-side with legacy architecture RANs, is the unified approach for engaging any automation solutions defined by O-RAN architecture and the RIC platform. Once we have a RIC platform up and running, we can use it for our advantage and cherry-pick automation solutions that suit our needs. A working ecosystem with competitive solutions is likely to drive innovation. More than that: together with partners, you may develop your own solutions for specific needs if you're an advanced MNO.
But here we face a challenge...
Given the complexity of the network with equally complex configurations and a vast range of services tailored to meet specific needs for enterprise customers, how do we dare to deploy an automation solution from a third party? A solution that inherently takes control over our network and starts to fiddle around with configuration data and critical parameters deep down in the RAN functionality, often without our knowledge?
O-RAN Automation Challenge
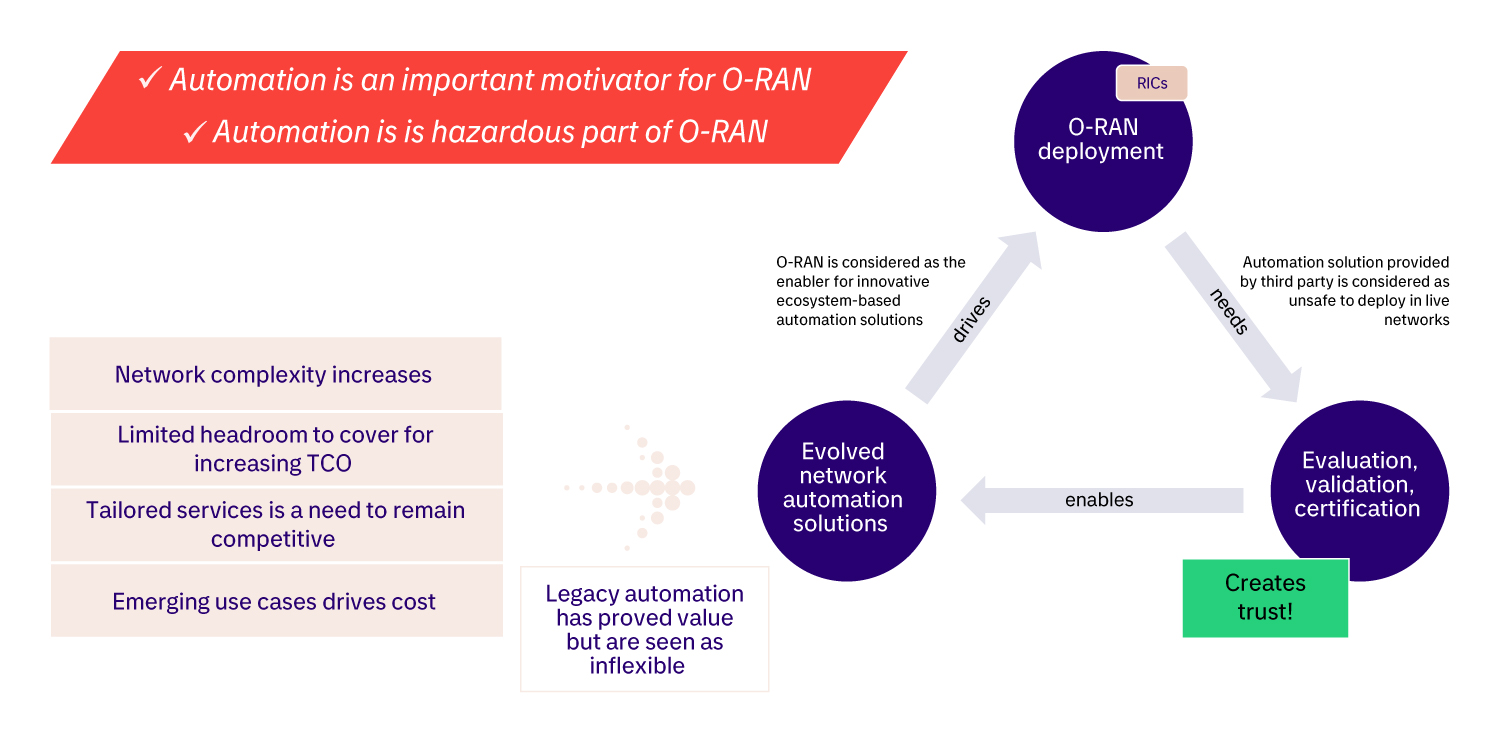
The driver for O-RAN based automation packed with promising features is apparently here. However, if we're not ready to use it just yet, should we stick with turnkey options from RAN vendors, as well as their generic solutions? Such setup will most likely work, but not always in the optimal way for specific network, customers, and operational procedures.
Another option would be to get what we want from a boiling and innovative ecosystem, and secure expected behavior of the automation solution before we deploy it in the live network.
Mitigate Risks – Create Trust
We can now see that finding means to validate automation solutions is a foremost goal for MNOs already with O-RAN networks or those planning to deploy them. To mitigate risks that come with deploying an automation solution in a live network, it should be first validated in a simulated environment that mimics major aspects of a real network and runs operational situations as realistically as possible. It should allow for modeling physical environment, network topology and traits, and user behavior.
Important model parameters include:
- Physical environment: geographic topology, buildings, infrastructure, geographic aspects that impacts radio conditions.
- Network aspects: cell topology, network and data center topology, dynamic radio conditions, forwarding capacity, active service configurations like slices and logical networks.
- User behavior: daily habits like roaming and service usage, but also specific scenarios that impact users’ behavior and network traffic accordingly, such as concerts, sport events, accidents, catastrophes, holidays, etc.
With such modeling capabilities, an MNO can set up a simulated validation environment that exhibits a behavior close to that of the real network. To allow for deep investigation of how different automation solutions behave and their impact on ongoing service delivery and resource utilization, the validation environment has to provide extensive means for KPI monitoring and analysis, both for network and user level.
Simulation-based testing also benefits vendors of automation solutions and xApps/rApps. With the addition of DevOps supporting capabilities, an automation solution vendor would be able to use the validation environment for staging tests on different levels for different types of tests, from individual unit tests of xApps/rApps to a hypothetical full-scale network run with hundreds of thousands of users. This will demonstrate to a solution vendor reduced time-to-market thank to a smooth working environment that supports a total range of tests, from initial research on algorithm development to system verification of complete automation solutions.
Carrying out acceptance tests for specific automation solutions in a simulated “digital twin” environment limits the need for costly, time-consuming, and even dangerous live network tests on the MNO’s side.
A smooth CI/CD chain supporting development, testing, and deployment of automation solutions, increases the development pace for specific solutions, and ensures the stability of a whole network. When tests validate correct behavior of any network automation solution, and secure that it enhances specific live networks without risking their service delivery, big cost savings could be foreseen, both MNOs and solution vendors can foresee big cost savings.
Moreover, the ability to play with different user scenarios and network topologies while observing an automation solution’s behavior will promote development of advanced automation solutions not possible without the simulation. On top of that, we can investigate the behavior of different concurrently running automation solutions, and identified issues that can be mitigated by design. This will ultimately allow for more efficient automation of the MNO’s network and lower operational costs.
Tietoevry Create’s Network Automation Validation Solution
We are dedicated to investing our efforts into developing the Network Automation Validation Solution (NWA-VS) that supports advanced validation, exploration, and research of O-RAN-based automation solutions.
Tietoevry Create's Network Automation Validation Solution
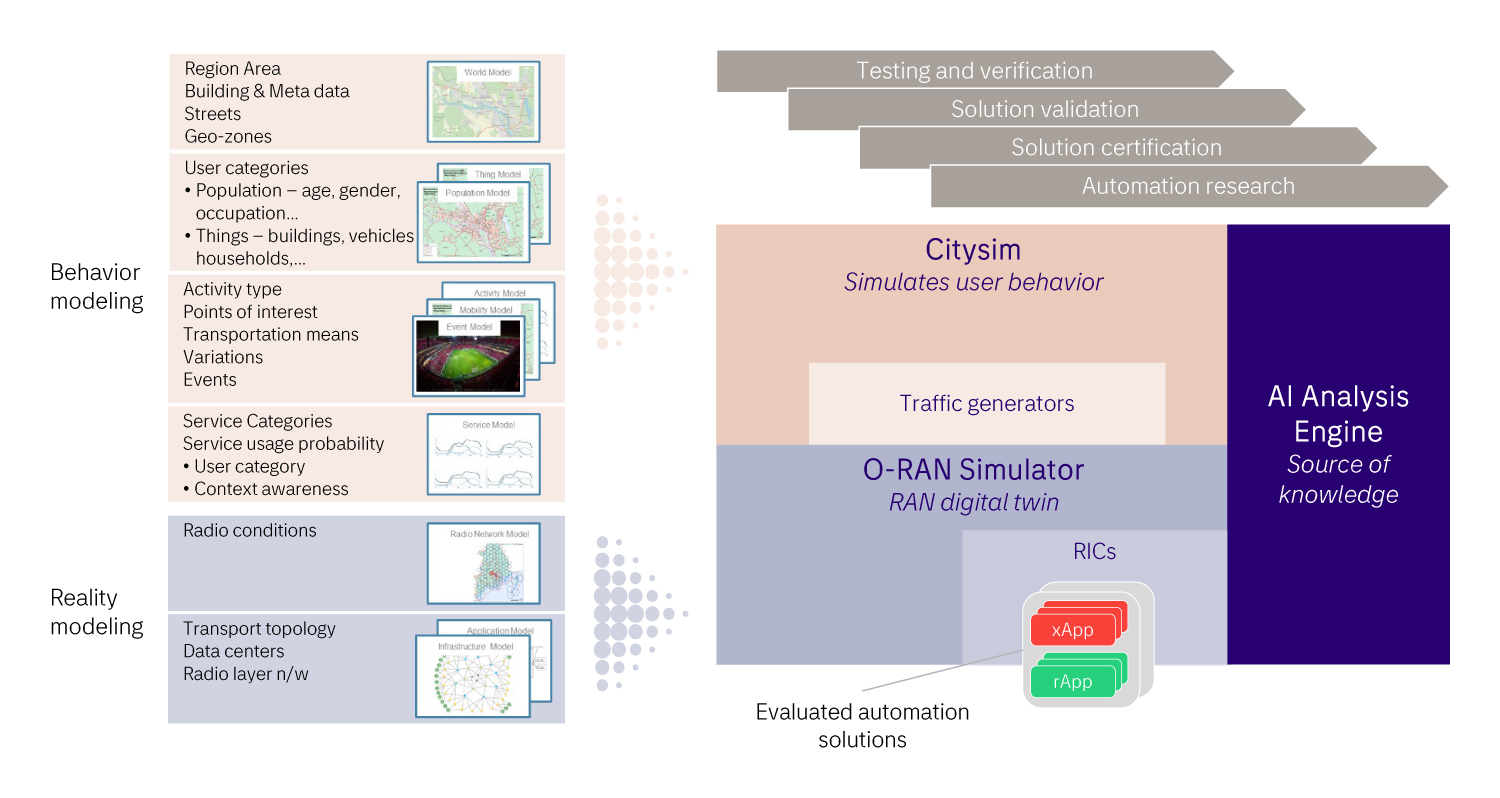
NWA-VS key components are:
- A highly scalable O-RAN Simulator that allows for setup of any full-scale hypothetical O-RAN or a digital twin of an existing O-RAN, all in the context of real society. The O-RAN Simulator allows for simulating networks with thousands of cells and provides means for KPI reporting from the emulated RAN functions. The standard interfaces towards the RIC platforms are supported according to O-RAN Alliance specifications.
- Citysim is a user behavior modeling and traffic generating tool that allows for modeling user behavior in terms of dynamic service usage, physical location, and roaming habits of hundreds of thousands of users. Citysim is responsible for cell selection based on simulated radio conditions for each user and can generate traffic according to the modeled service usage . Each user’s service usage can be monitored with a set of KPIs. Citysim allows for modeling both day-by-day regular behavior scenarios as well as extraordinary and extreme scenarios like major society crises, accidents, etc.
- The RIC Platform, i.e. near-RT RIC and non-RT RIC, which integrate the automation solutions into the simulated environment. NWA-VS targets a portfolio of RICs to allow for testing rApps/xApps towards different RICs and evaluate their compatibility, or to setup an MNO staging environment with the precise RICs that the MNO employs in its live RAN.
- The AI Analysis Engine analyses the outcome of different test and validation cases. For this, the behavior of the RAN (KPIs) as well as of the Apps (software logs) are investigated by AI/ML algorithms. By analyzing real-time data, the AI Engine learns normal RAN operations, and then can detect and analyze anomalies that appear during the deployment of different automation solutions. Automation solutions that exercise the AI approach are inherently difficult to analyze without AI, because of the lack of static rules controlling the behavior. So, we apply a “validating AI by AI” methodology. By utilizing AI to analyze and validate test results, we ensure that the solutions are not only optimized for peak performance, but can also continuously adapt to changing network conditions in real-time.
NWA-VS features a management system to control and monitor different tests, and supports the processing of KPI reports from both the O-RAN Simulator and Citysim. Here are some examples of activities you can improve with Tietoevry Create’s NWA-VS:
- Investigate the gains in terms of selected service and network level KPIs that a specific network automation solution would exhibits if applied to a part of or a full live network.
- Verify that a specific automation solution is robust and maintains its specified behavior during extraordinary conditions, like extensive network failure or major society events like crises, accidents, concerts etc.
- Evaluate how multiple different and concurrently active automation solutions will coexist.
- Verify the functionality and performance of specific automation solutions or individual rApps/xApps operating in full-scale RAN.
- Research the behavior and characteristics of automation algorithms applied to different traffic scenarios and network setups.
- Certify third-party rApps/xApps to use in MNO’s live network.
- Evaluate the impact of different parameter settings for a specific automation solution in a range of network and traffic scenarios.
- Evaluate automation solution compatibility with O-RAN standards and different RIC products.
DevOps Way-of-Working
MNOs and automation solution vendors both need a simulated full-scale, realistic traffic environment, but each from a somewhat different angle. The MNO will ultimately make use of a digital twin of its real network, a customer base, and historical traffic data for modeling users generating traffic to feed that digital twin. On the other hand, a solution vendor benefits from different generic “type” networks (e.g. different sizes, rural/urban, etc.) and modeling stereotypic user behavior, possibly aligned with specific regions or cities of the world. When looking at NWA-VS from a DevOps perspective, it can become the enabler for a highly efficient CI/CD chain that supports secure provisioning and deployment of new automation solutions.
CI/CD for Development, Validation, and Deployment of Automation Solutions
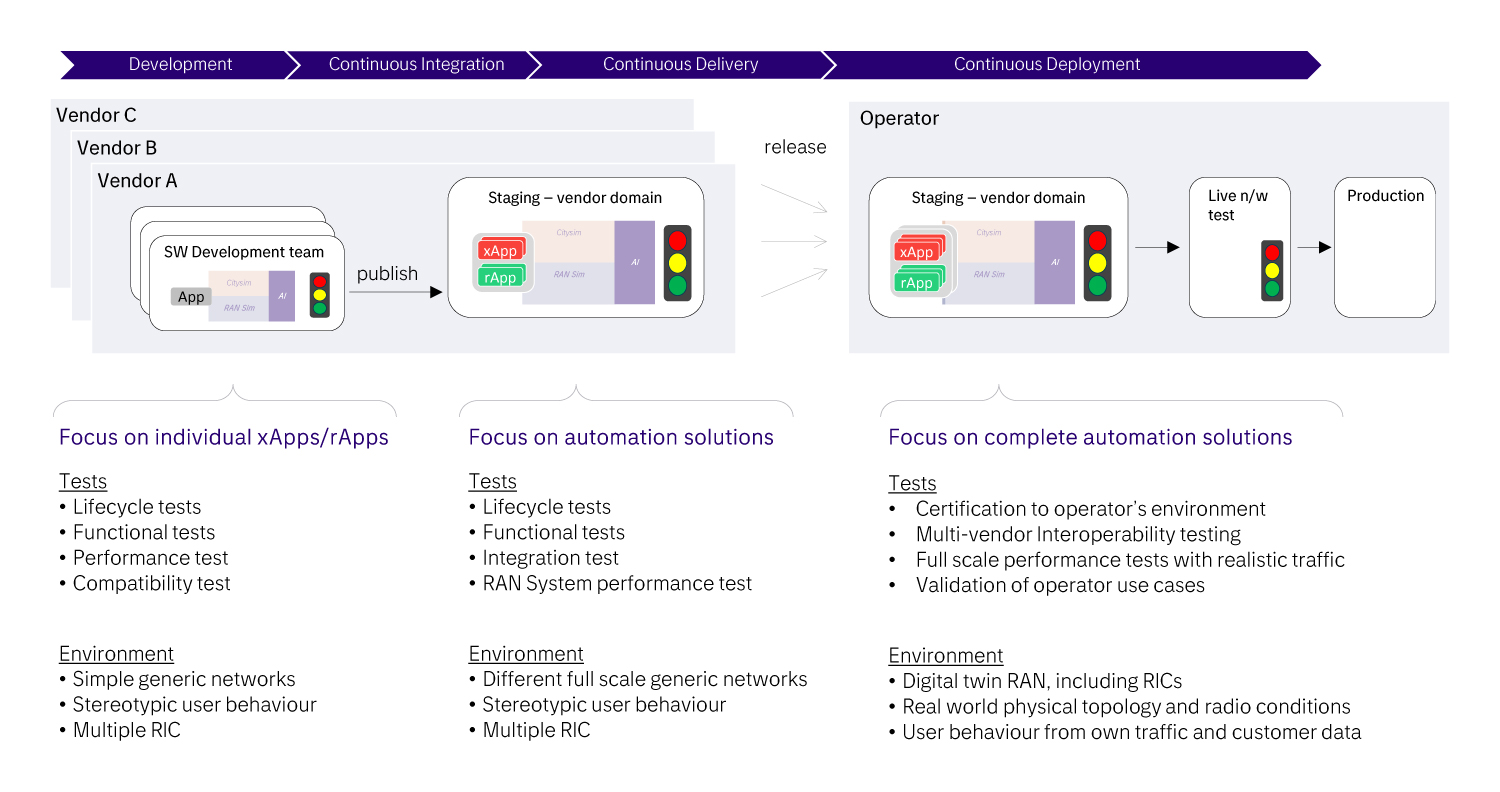
A common ground for both vendors and MNOs using them in their live network will be established by the support for a single automated CI/CD chain starting at the vendor’s software development – possibly on cue from the MNOs and according to their requirements – and ending when the solution is active in the MNO’s live network. It is even possible for an MNO to orchestrate an ecosystem with many solution providers, all being part of the same CI/CD chain. Such an integration of the different staging environments and different vendors will allow for smooth sharing of the models needed to establish the testing environment and enable a solid and unified surrounding for all the stages of the CI/CD process.
Tietoevry Create’s Initiative
In support of the growing O-RAN ecosystem, and with focus on automation solutions, Tietoevry Create is launching its NWA-VS platform. The goal is to provide MNOs or their appointed system integrators and automation solution vendors with the means to research, develop, evaluate, and validate the behavior of complete automation solutions, as well as individual rApps/xApps in a simulated yet realistic environment. There are several ways we can use Tietoevry Create’s platform.
- The Lab-as-a-Service approach gives access to the platform as running on Tietoevry Create’s premises. This gives our customers access to all the features of the platform, while leaving the burden of maintaining such an environment to our team.
- A licensing agreement allows for running the NWA-WS platform on customers’ premises with support – possibly on-site – from Tietoevry Create. The support will assist the customer with defining the infrastructure needed, deploying the platform, and keeping the environment operational.
- On Time & Material basis, Tietoevry Create may:
- Develop and specify test cases for support of any test scenario. This could be done on tight cooperation with the customer and on specific requirements from the customer, or as a total offering where Tietoevry Create also define the needed test cases.
- Setup and execute tests, either as add on to a licensing agreement or within a LaaS setup.
- Taking on the lead for continuous coordination and operation of a DevOps toolchain.
- Develop specific features tailored to meet unique need of individual customers.
In Conclusion
Tietoevry Create offers a solution for research, evaluation and validating of automation solutions for O-RAN networks. This is based on Tietoevry Create’s Network Automation Validation Solution (NWA-VS), that provides for full scale RAN simulation being the subject for network wide realistic traffic from users, who’s natural behavior in roaming and service usage is simulated in scale.
Tietoevry Create invites any MNO, vendor, or anyone else that see a value in our solution to engage with us to discuss how NWA-VS can meet your specific needs for developing and validating automation solutions in different realistic contexts. Tietoevry Create sees different opportunities here like pilot programs for potential customers to experience our solution firsthand and to investigate what is potentially needed to meet specific needs, or a partnership co-development project, within which specific and tailormade features are developed to fulfil the partner’s requirements.
Learn more about our expertise in innovative telecom solutions!

Arne has 30+ years of experience across multiple technologies throughout the telco domain. He started his carrier in the transport and packet data industry, and over time has embraced O&M, operational processes, wireless/mobile networks, network virtualization and network automation as his areas of expertise.



